A Level Physics builds on concepts from GCSE and introduces students to a broader and deeper understanding of the universe, from the smallest particles to the largest structures. With so many new topics, equations, and practical skills to cover, it is easy to feel stressed.
Whether you are just starting or preparing for exams, having a clear overview of the A Level Physics syllabus and the A Level Physics topics list syllabus can make all the difference. Knowing what to focus on will help you organise your A Level Physics notes and plan effective A Level Physics revision strategies.
Across all exam boards, A Level Physics content is divided into fundamental topics like mechanics, waves, and electricity, and advanced fields such as nuclear physics, astrophysics, and particle physics. This article gives clarity on how AQA A Level Physics, Pearson Edexcel A Level Physics, and OCR structure their courses, and links to Mixt Academy’s trusted resources, including Physics A Level past papers and A Level Physics equations/formulas, to help you feel in control.
For a full introduction to the subject and why it matters, see What is A Level Physics? | Topics, Exams and How to Get Top Grades.
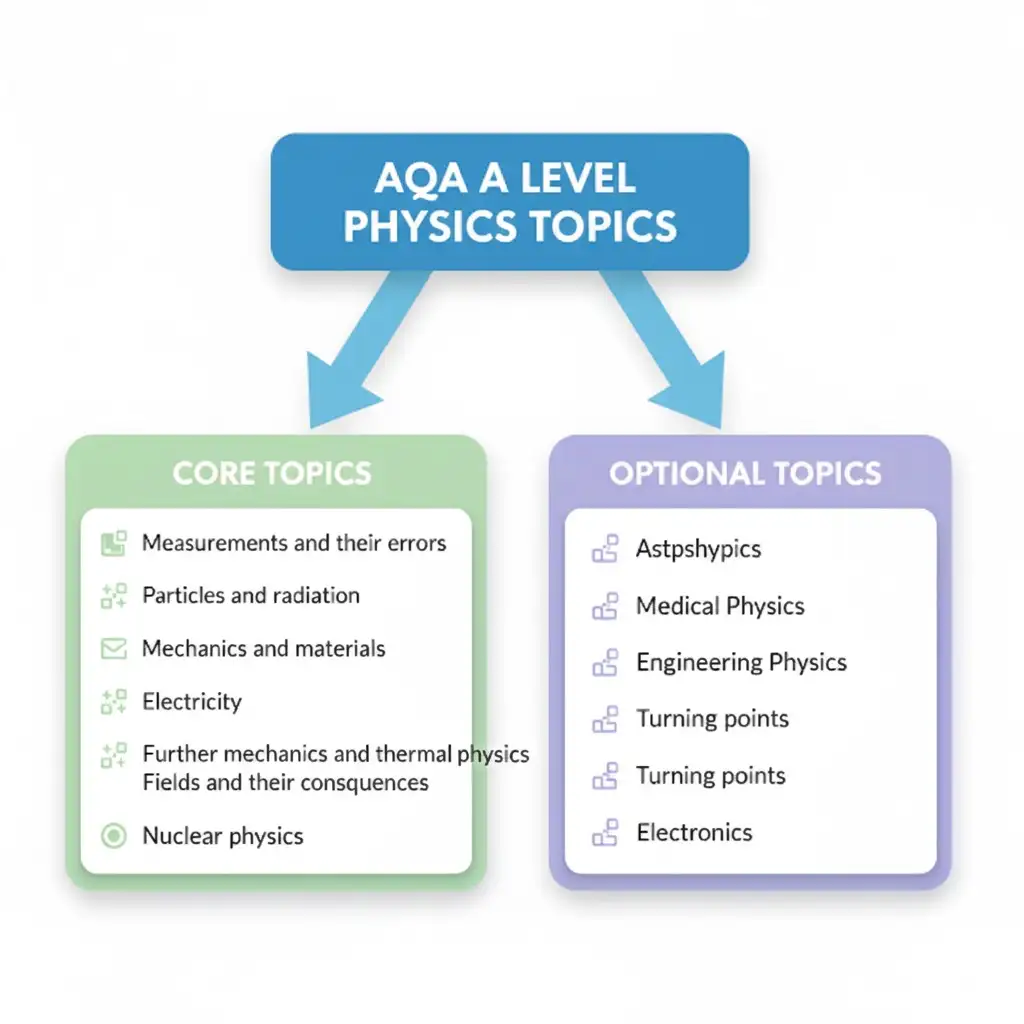
This section focuses on how to measure physical quantities with accuracy and consistency. You will work with SI units, standard prefixes, and methods to reduce and account for experimental error. Estimating values and handling uncertainties will build your practical work throughout the course. Topics include:
In this section, you will learn the structure of atoms, from protons and neutrons to quarks and leptons. You will study particle interactions, the role of exchange particles, and how antimatter fits into the bigger picture. The photoelectric effect and wave-particle duality are also introduced, marking the start of your journey into quantum physics. Topics include:
GCSE studies of wave behaviour are extended in this topic through a detailed look at the properties and applications of both travelling and stationary waves. You will learn how waves interact through refraction, diffraction, superposition, and interference, and explore how these phenomena apply to light, sound, and other types of waves. Topics include:
This topic begins with an introduction to vectors and builds your understanding of forces, energy, and momentum. It then moves on to explore the properties of materials, including their strength, elasticity, and how they respond to stress. Topics include:
This section builds on GCSE knowledge of electric circuits and explores them in greater depth. You will learn how current, potential difference, and resistance are related in ohmic and non-ohmic components. You will explore complex circuits, including internal resistance and the use of potential dividers in sensing systems. Topics include:
This section is divided into two parts: Section 6.1, Periodic motion and Section 6.2, Thermal physics. Section 6.1 focuses on periodic motion, including circular motion and simple harmonic motion (SHM). You will study systems such as springs and pendulums, and learn how to analyse their oscillations, energy transfers, and resonance effects.
Section 6.2 develops your understanding of heat, temperature, and internal energy. You will explore thermal energy transfers, apply the gas laws, and use molecular kinetic theory to describe the behaviour of ideal gases. Topics include:
This section unifies different types of fields (gravitational, electric, and magnetic) through common principles. You will explore how forces act at a distance, the energy associated with fields, and how fields influence the motion of masses and charges.
The topic also looks at practical applications such as capacitors, induction, and transformers, highlighting the significance of these fields in real-world systems, such as power transmission. Topics include:
This section builds on section 2, Particles and radiation, and explores the internal structure of atomic nuclei. You will study different types of radiation, nuclear reactions, and how mass is converted into energy in nuclear processes, such as fission and fusion.
You will develop an understanding of the physics behind nuclear energy production, as well as its broader implications and impact on society. Topics include:
This section applies physics to the universe beyond Earth. You will study how telescopes work, how stars are classified, and how their properties are determined using physical laws. The topic explores the life cycles of stars from formation to death, including the extreme conditions of supernovae, neutron stars, and black holes.
You will also look at evidence for the expanding universe and study cosmology through redshift, Hubble’s law, and the Big Bang theory. Topics include:
This section explores how physics is used in medical imaging and treatment. You will study how lenses are used to correct vision, how X-rays and ultrasound produce diagnostic images, and how radioactive tracers and gamma cameras are used in nuclear medicine. Topics include:
This section focuses on applying physics principles to rotating systems and engineering contexts. You will study rotational motion, the laws of thermodynamics, and applications of engines in the real world. Topics include:
This section covers the experiments and discoveries that led to quantum theory and modern physics. You will study the discovery of the electron, the photoelectric effect, wave-particle duality, and how Einstein’s theory of special relativity emerged. Topics include:
This section introduces the fundamentals of analogue and digital circuits. You will study a range of individual components and explore both analogue and digital systems, from operational amplifiers to digital signal processing. You will also look at the key issues in data communication. Topics include:
If you are revising for the AQA A Level Physics exam, Mixt Academy has created a complete set of resources that are precisely aligned with the official specification. Our expert-written revision notes, exam-style questions, and Physics A Level past papers, aligned with the A Level Physics syllabus, help students practise A Level Physics equations/formulas and consolidate learning efficiently and prepare with confidence. For detailed revision strategies, see How to Revise for A Level Physics in 2026? Learn Smartly.
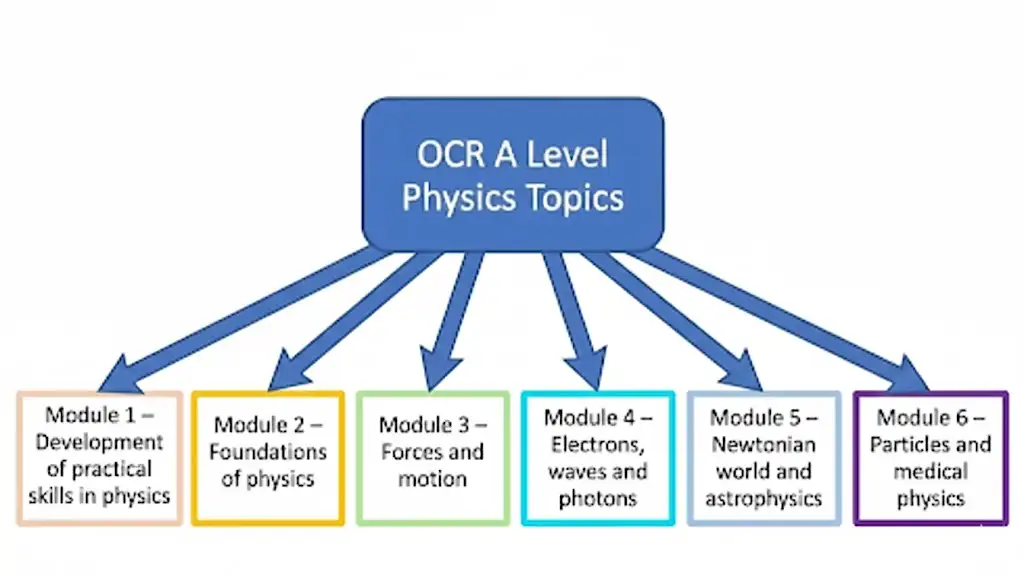
OCR A Level Physics is divided into six teaching modules:
Physics is an experimental subject at its core, and this module helps you develop the practical skills that support everything you will do throughout the A Level course. You will learn how to plan experiments, take accurate measurements, analyse data, and evaluate results. Module 1 is divided into two parts:
Together, these two sections help you build a strong foundation in experimental science, giving you the tools to succeed in both exams and hands-on work.
This module introduces the fundamental conventions and concepts that build the entire course. You will learn how physicists define and use physical quantities, SI units, and vector and scalar quantities to communicate ideas clearly and precisely. It also covers how to make measurements, analyse data, and handle uncertainties, skills that are essential for both theory and practical work throughout the A Level Physics. Topics include:
This module explores how forces influence the motion and shape of objects. You will learn how to model and analyse motion in one and two dimensions using mathematical techniques, apply Newton’s laws to various scenarios, and investigate how forces result in energy transfer and deformation.
It also develops your understanding of materials through topics like density, stress, strain, and the Young modulus, alongside the conservation of momentum and the physics of collisions. This module underpins many real-world applications and supports the development of both conceptual and practical skills. Topics include:
This module introduces the key ideas of quantum physics, starting with a foundation in electricity and wave behaviour. You will study electric charge, current, and resistance, as well as wave properties like diffraction and interference. These topics set the stage for understanding the dual wave–particle nature of light and matter, which forms the basis of quantum theory.
Before exploring quantum effects in depth, you will build your understanding of electrical circuits and electromagnetic waves. This module also encourages you to reflect on how quantum physics developed historically and the role of experiments in validating scientific ideas. Topics include:
This module highlights how Newton’s laws of motion continue to explain the physical world, from the microscopic motion of particles in gases to the large-scale movement of planets and galaxies. You will explore how models based on Newtonian mechanics help us understand thermal physics, circular motion, and oscillations.
The final section broadens your view to astrophysics and cosmology, using electromagnetic observations to explore the life cycles of stars and the expansion of the universe. The module highlights the importance of observation and evidence in shaping scientific models over time. Topics include:
This module brings together advanced topics in electricity, fields, and nuclear physics, and introduces students to applications in medicine. You will explore how capacitors store and discharge energy, how electric and magnetic fields influence charged particles, and the principles of electromagnetism.
In the final sections, you will focus on nuclear structure, radioactivity, and how fundamental particles interact. You will also study the physics behind medical imaging technologies, such as X-rays and PET scans. Topics include:
OCR resources include A Level Physics notes, A Level Physics revision, and guidance on Everything About A Level Physics Papers and Exam Preparation for understanding exam structure and mark allocation.
Mixt Academy offers a full suite of resources designed to the OCR specification. From clear revision notes to practice questions and past papers, everything is designed to help you strengthen your knowledge and make you feel ready for the exam:
Our A Level Physics tutors explain concepts step by step and boost your confidence.
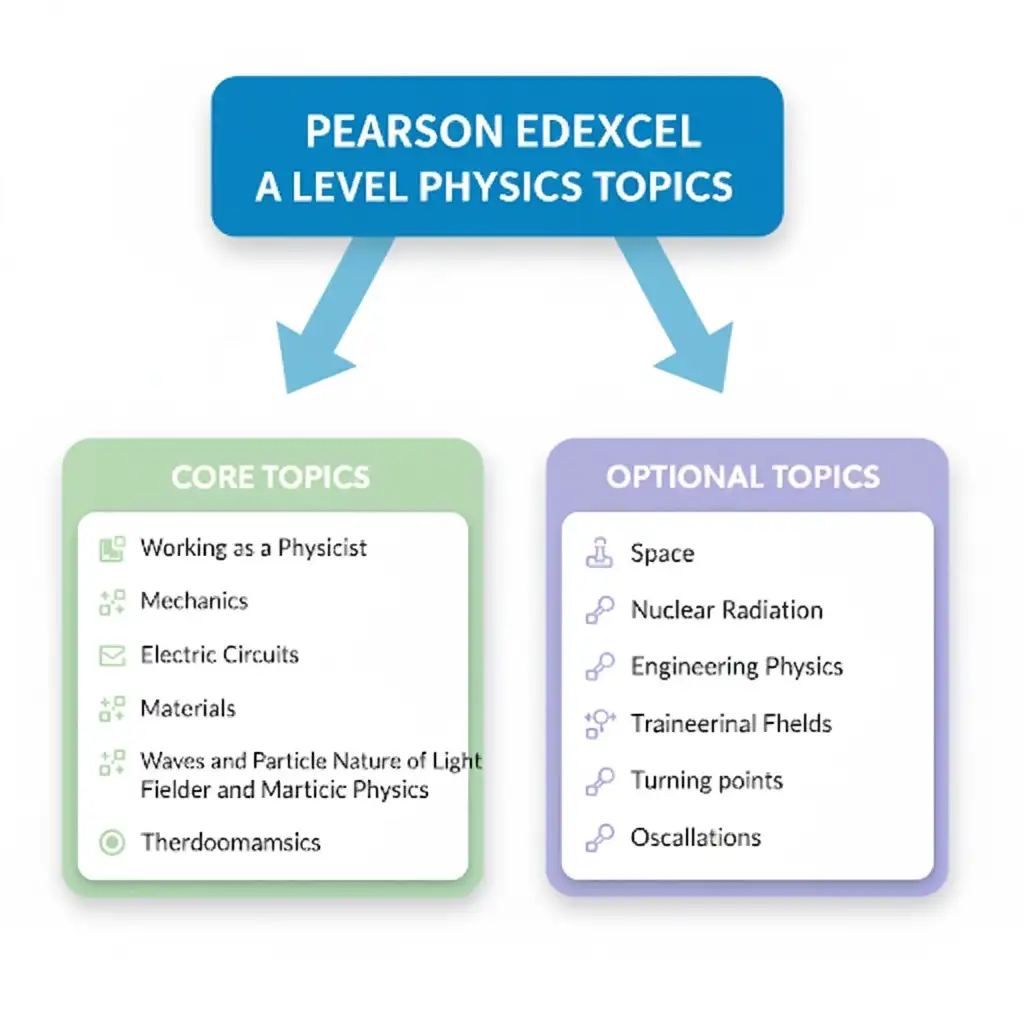
Physics relies on precise measurement, critical thinking, and evidence-based reasoning. This topic develops your understanding of how physicists work, including how they use data, design experiments, and evaluate claims. Topics include:
This topic introduces the fundamental principles that govern motion and forces. You will learn how to describe and analyse movement, apply Newton’s laws, and understand energy transformations. Topics include:
In this topic, you will explore how electric currents behave in different circuits, including how resistance changes and how energy is transferred. Topics include:
This topic covers the mechanical behaviour of solids, including deformation, stress and strain, and the properties of materials used in real-world applications. Topics include:
In this topic, you will study the properties of waves, including light and sound, and discover how quantum theory helps explain phenomena like the photoelectric effect. Topics include:
This topic builds on the earlier mechanics topic by exploring momentum, collisions in two dimensions, and circular motion, which are helpful in many real-world and particle physics contexts. Topics include:
This topic explores how charges interact through fields, both static and changing, and how this leads to technologies such as capacitors and motors. Topics include:
This topic investigates the smallest components of matter and the forces that guide them. You will examine the standard model and particle interactions. Topics include:
In this topic, you will explore the concepts of heat, internal energy, and how temperature relates to particle behaviour. Topics include:
This topic introduces key concepts in astrophysics, including how we study stars, measure astronomical distances, and interpret radiation from space. Topics include:
This topic explores how unstable nuclei undergo radioactive decay and how the properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation differ. You will also study nuclear binding energy, exponential decay laws, and how to analyse half-life and activity. Topics include:
Achieve your best possible grade with Mixt Academy. Find expert-written A Level Physics revision resources, specifically designed for your exam board. This includes detailed revision notes and past papers with mark schemes.
For exam preparation, it is helpful to check the A Level Physics grade boundaries to compare performance across boards and to plan which topics need more focus. Using A Level Physics notes, practising A Level Physics equations/formulas, and working through Physics A Level past papers ensures students are confident and ready for all exam formats, whether studying AQA A Level Physics, Pearson Edexcel A Level Physics, or OCR.
With the right combination of guidance, structured revision, and exam practice, mastering A Level Physics is not only achievable it can also be enjoyable and rewarding, opening doors to further STEM studies and careers.
Follow our expert A Level Physics guides to study smarter, not harder.
The content of the course covers measurements and their errors, particles and radiation, waves, mechanics and materials, electricity, further mechanics and thermal physics, fields and their consequences and nuclear physics.
It can be challenging due to theory, practicals, and maths. Still, consistent use of A Level Physics notes, A Level Physics equations/formulas, and Physics A Level past papers makes it manageable.
Main boards are AQA, Pearson Edexcel, OCR, and CIE. Refer to the Cambridge A Level Physics syllabus or Edexcel A Level Physics specification for details.
Use structured A Level Physics revision plans, A Level Physics notes, A Level Physics equations/formulas, and Physics A Level past papers to revise effectively.
Achieving an A or A* in A-level Physics requires a combination of strong mathematical skills, effective revision techniques, strategic exam preparation, and proficiency in practical work.

Mixt Academy is a global online tutoring platform that connects students with expert IGCSE, GCSE, and A-Level tutors for one-to-one learning. With flexible scheduling, personalized lesson plans, and experienced teachers from top curricula, Mixt Academy helps students strengthen concepts, improve exam skills, and achieve higher grades with confidence.
IGCSE Chemistry Papers: Common Mistakes & Exam Tips This IGCSE…
IGCSE Extended vs Core Tiers: How to Pick the Right…
Last Month Before IGCSE Exams: A Complete Study Plan Are…
Understanding GCSE Grade Boundaries and How to Prepare? Grade boundaries…
Differences GCSE English Language vs English Literature GCSE English is…
What is GCSE? A Guide for International Students & Parents…
Top Benefits of Completing AS and A Levels Privately Explore…
IB Math: Strategies for Achieving a Level 7 Learn expert…
How to Use OCR Past Papers for Effective Revision? Past…
Complete Guide to the AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification Understanding the…
Everything Students and Parents Must Know About AQA Exams Choosing…
AQA vs Cambridge: Comparing UK and International Exam Boards When…
Hire an Expert Tutor from Just 15$/hr