Light is an important part of our lives. We see colours, shapes, and objects because light travels and reaches our eyes. If there were no light, everything would be dark and unclear. However, light reacts differently with everything it comes into contact with. Some materials let light completely pass through, while some let it pass only partially. Others completely block light.
Because every material reacts differently with light, scientists decided to classify materials into 3 categories: transparent, translucent, and opaque. Understanding this is one of the first steps to understanding light and vision. It is something everyone learns in primary and middle school, and it has to do with real life.
In this blog, you will learn what transparent, translucent, and opaque mean. You will also learn what the differences are between transparent, translucent, and opaque materials, and what transparent, translucent, and opaque objects are in everyday life. You will learn about light transmission in materials and how it connects to the properties of materials. You will also learn about how Mixt Academy helps students with these concepts.
At Mixt Academy, our expert tutors explain these concepts using clear examples, diagrams, and real-life demonstrations.
Based on how much light can pass through them, materials can be grouped into 3 categories called transparent, translucent, and opaque materials. When light strikes an object, it may do one of the following:
Because of these behaviours, materials can be categorised into three different classes: Transparent materials, translucent materials, and opaque materials.

Light that hits transparent materials can pass through without being blocked or scattered, and as a result, the objects behind transparent materials can be seen clearly and sharply.
Common “examples of transparent, translucent and opaque objects” that are transparent include:
For example, you can always see what is on the other side of a glass of water because light travels straight through the material. Transparent materials are utilised in homes, vehicles, laboratories, and in a number of optical instruments.

Some light can only be allowed to pass through translucent materials. However, the light that can cross is scattered in different directions, and this makes objects behind them unclear.
A translucent material is one that allows light to pass through it, but does not allow clear images to be seen through it. Examples are:
For instance, bathroom windows are often made of frosted glass. They allow sunlight to enter while maintaining privacy. It allows light to come through it while blocking people’s view. You can see some shapes and colours, but not a clear image. Learning to identify translucent materials is very important for understanding the light transmission of materials and the formation of shadows.

Opaque materials are those that do not allow light to pass through them. When light hits an opaque object, the light is either reflected or absorbed.
5 Examples of Opaque Materials
Some everyday opaque materials include:
Walls, doors, books, and tables are also opaque. Because opaque materials block light completely, they are essential for shadow-making.
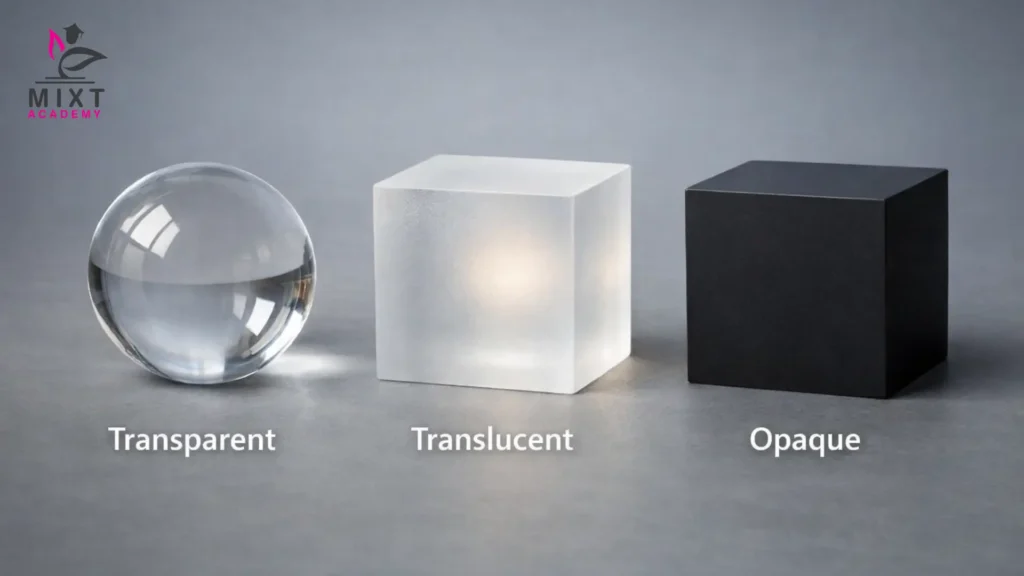
The difference between transparent, translucent and opaque materials becomes clear when we compare how they interact with light. Comparing the opaque, translucent, and transparent materials helps demonstrate how they each react to light.
Difference Between Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Materials
Property | Transparent | Translucent | Opaque |
Light passing | Almost all | Some | None |
Visibility | Clear | Blurry | Not visible |
Shadow formed | Very faint | Soft | Dark |
Light transmission in materials, or light transmission, is a term that describes how light passes through a material. Different materials all react differently to light depending on the structure and thickness of the material.
This concept is essential for understanding:
It also explains why some materials are chosen for windows, while others are used for walls.
Light behaves differently with varying properties of materials. Some of these are:
For example:
These properties are what scientists use to determine materials for use in construction, lenses, screens, and lamps.
This idea of light being absorbed or transmitted also helps students understand concepts beyond materials on Earth. A common question students ask is which is the hottest planet. Venus is the hottest planet because its thick atmosphere absorbs and traps heat instead of allowing it to escape. Just like opaque materials absorb light, Venus absorbs heat energy, making it hotter than even Mercury.
We use these materials every day, often without realising it.
Transparent materials are used in:
Translucent materials are used in:
Opaque materials are used in:
Observing “transparent translucent and opaque objects” in daily life makes science more practical and meaningful.
Students commonly confuse the use of transparent and translucent materials. Some of these mistakes include:
These mistakes can easily be avoided with the use of clear explanations.
At Mixt Academy, we believe in helping students understand the science behind the words, rather than just memorising them. We use visuals to teach about transparency, translucency, and opacity, and we explain them interactively.
Our tutors provide clear explanations that help students understand the difference between transparent, translucent, and opaque materials. They teach students how to use this knowledge in their exams and everyday lives.
To assist in the deepening of learning, parents can encourage children to do the following:
Going through these learning activities with children can enhance the learning process and provide parents with stress-free learning activities to do with their children if they follow the suggestions made by Mixt Academy tutors.
Our tutors provide step-by-step guidance and tips to score better in exams.
Students are often required to answer questions regarding the terms ‘transparent, translucent, and opaque’ that are frequently used in international curricula such as the GCSE, IGCSE, IB, AP, and A Level. These types of questions are used to evaluate a student’s understanding and knowledge regarding the transmission of light through objects, the practical use of materials, and the properties of materials.
The following questions can help you prepare to answer questions that are typically seen on past exams. Each answer has been written in the style that students are expected to use when answering the questions.
Question (GCSE / IGCSE):
Classify the following materials as transparent, translucent, or opaque. Give a reason for each answer.
Model Answer:
What the Examiner Looks For:
Question (GCSE / KS3):
Explain why opaque objects form dark shadows when light falls on them.
Model Answer:
Opaque objects form dark shadows because they block all the light falling on them. Since light cannot pass through an opaque object, a dark area is formed behind it, which is known as a shadow.
What the Examiner Looks For:
Question (IB MYP):
Explain how the internal structure of a material affects whether it is transparent, translucent, or opaque.
Model Answer:
The internal structure of a material affects how light passes through it. In transparent materials, particles allow light to pass through easily. In translucent materials, light is scattered due to uneven particle arrangement. In opaque materials, light is absorbed or reflected, so it does not pass through.
What the Examiner Looks For:
Question (AP Level):
A student shines a flashlight at three objects: clear plastic, wax paper, and a metal sheet. Describe what the student observes and explain why.
Model Answer:
The clear plastic allows most of the light to pass through and is therefore transparent. The wax paper allows some light to pass through but scatters it, making it translucent. The metal sheet blocks all the light, so it is opaque.
What the Examiner Looks For:
Question (A Level):
Describe the difference between transparent and translucent materials in terms of light transmission.
Model Answer:
Transparent materials allow light to pass through with little or no scattering so that images can be seen clearly. Translucent materials allow light to pass through but scatter it in different directions, resulting in blurred images.
What the Examiner Looks For:
Exam Preparation Tip for Students
Examiners all over the board expect the same from students:
Answering these structured questions helps the learning of the opaque, translucent, and transparent concepts and boosts performance in exams.
Understanding transparent, translucent and opaque materials is not just another science lesson: it’s about learning to observe the world. The materials around us, from our walls and books to our curtains and windows, control how we see and experience light every day. When students learn the concept of light transmission in materials and the properties of materials, it helps them see the logic and excitement in science rather than the confusion.
At Mixt Academy, students learn to master the concepts in a way that allows them to learn the concepts, not just understand them. It helps them to develop a strong foundation, which boosts confidence. Start your journey to learning with Mixt Academy and bring clarity to the confusion.
Mixt Academy offers personalised online tutoring, tailored to your pace and learning style.
These terms describe how materials interact with light. Transparent materials allow almost all light to pass through, translucent materials allow some light, and opaque materials block light completely. This classification helps us understand shadows, visibility, and material usage in daily life.
A translucent material allows light to pass but scatters it. This makes objects behind it appear unclear. A common example is frosted glass, which lets light in but does not allow clear images.
The three types are transparent, translucent, and opaque. Each type differs based on the amount of light transmitted through the material.
Five examples of opaque materials are wood, metal, stone, brick, and cardboard. These materials block light completely and form dark shadows.
Yes, a material can change based on thickness or surface treatment. For example, clear glass becomes translucent when frosted, and thin plastic may become opaque when layered.
Opaque objects block light completely. When light cannot pass through an object, a dark area called a shadow is formed behind it.
Yes, the air is transparent. It allows light to pass through completely, which is why we can see objects clearly through the air.

Mixt Academy is a global online tutoring platform that connects students with expert IGCSE, GCSE, and A-Level tutors for one-to-one learning. With flexible scheduling, personalized lesson plans, and experienced teachers from top curricula, Mixt Academy helps students strengthen concepts, improve exam skills, and achieve higher grades with confidence.
IGCSE Chemistry Papers: Common Mistakes & Exam Tips This IGCSE…
IGCSE Extended vs Core Tiers: How to Pick the Right…
Last Month Before IGCSE Exams: A Complete Study Plan Are…
Understanding GCSE Grade Boundaries and How to Prepare? Grade boundaries…
Differences GCSE English Language vs English Literature GCSE English is…
What is GCSE? A Guide for International Students & Parents…
Top Benefits of Completing AS and A Levels Privately Explore…
IB Math: Strategies for Achieving a Level 7 Learn expert…
How to Use OCR Past Papers for Effective Revision? Past…
Complete Guide to the AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification Understanding the…
Everything Students and Parents Must Know About AQA Exams Choosing…
AQA vs Cambridge: Comparing UK and International Exam Boards When…
Hire an Expert Tutor from Just 15$/hr