Trigonometry is a part of mathematics that helps us understand angles and sides of triangles. At first, it may look difficult, but when learned step by step, it becomes easy and interesting. Trigonometric ratios help students measure heights, distances, and angles using simple formulas. In this guide, you will learn trigonometric ratios, identities, formulas, and solved examples in a clear and simple way. This will help you build strong basics and feel more confident in math by Mixt Academy’s online maths tutors.
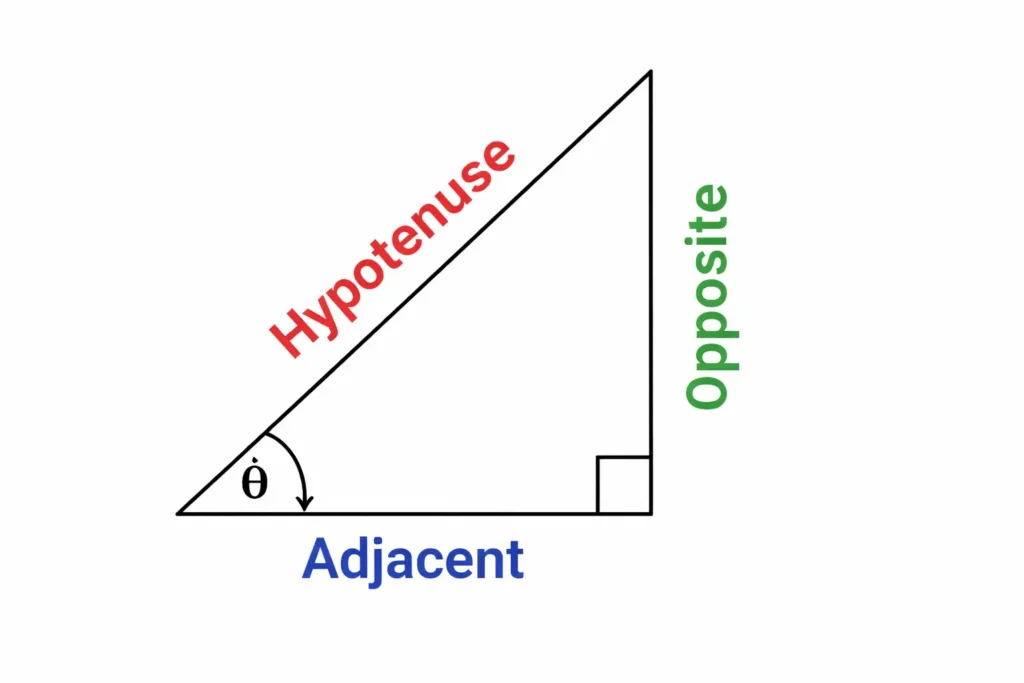
Trigonometric ratios are right-angled triangle functions that show the relationship between angles and sides.
The following are the topics trigonometry covers:
Trigonometry in Mathematics develops core skills like problem-solving abilities, logical and analytical thinking, a strong foundation of advanced mathematics, critical thinking, and spatial reasoning.
If we have a right-angle triangle, the length of each side of the triangle tells how steep or wide the given angle is, and trigonometric ratios are the simple comparison of those side lengths of the angle. The basic trigonometric ratios include sine, cosine, and tangent. However, other trigonometric ratios include cosec, sec, and cot.
In a right-angle triangle (an angle = 90°), find out
Identifying adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse will help you find trigonometric ratios.
For Example
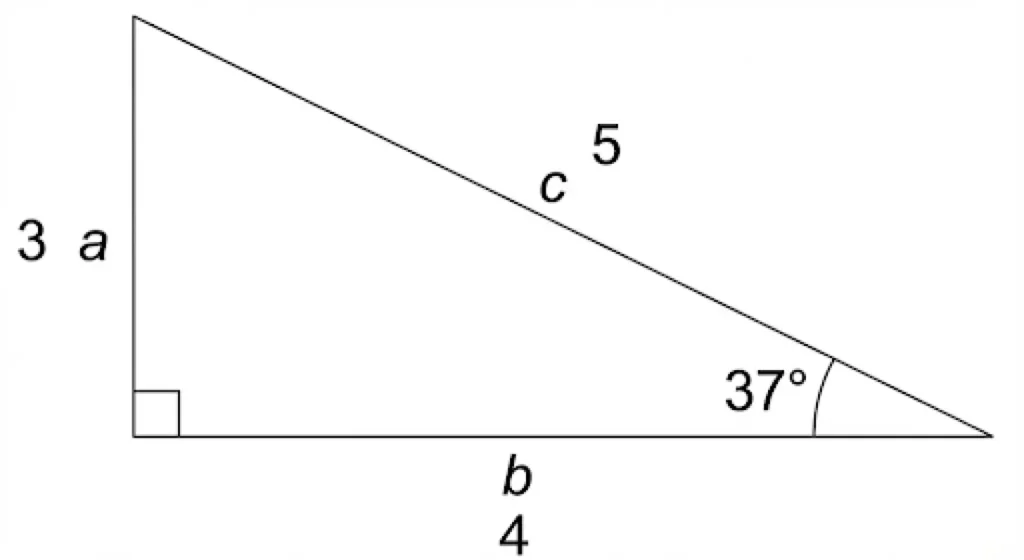
In the above given right-angle triangle
c = Hypotenuse = 5
a = Opposite = 3
b = Adjacent = 4
The trigonometric ratios for the above right-angle triangle will be
sin (37°) = opposite/hypotenuse = 3/5
cos (37°) = adjacent/hypotenuse = 4/5
tan θ = opposite/adjacent = 3/4
Learn sine, cosine, and tangent easily with one-on-one tutor support.
SOH-CAH-TOA is a simple way to learn how to memorize trigonometric ratios without confusion.
Besides the core three sine, cosine and tangent, other trigonometric ratios include Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant.
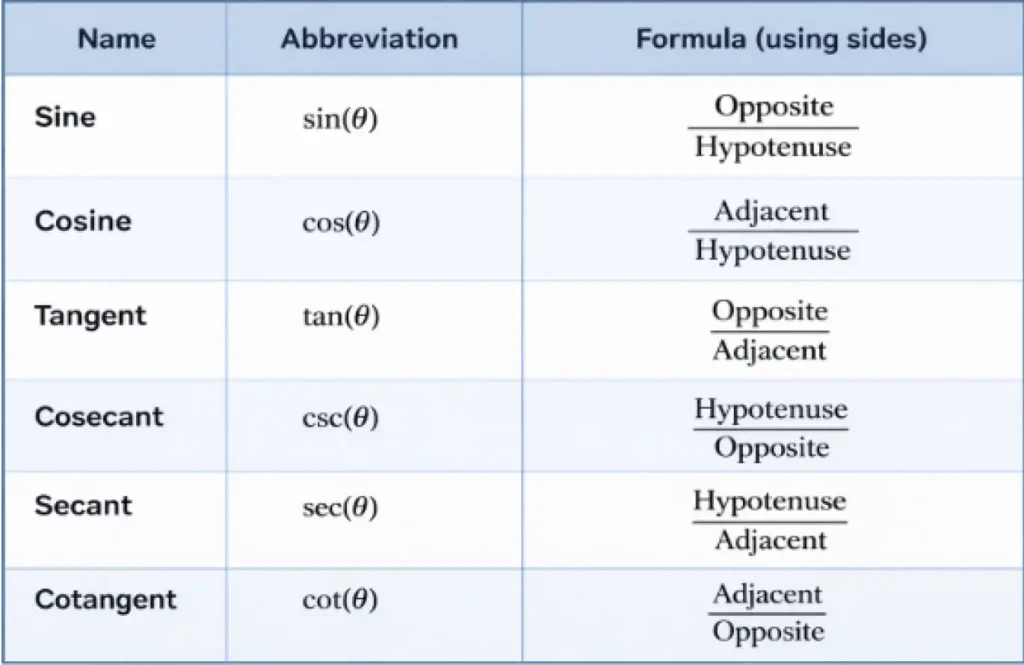
As we know how to find hypotenuses, perpendicular or opposite (same), and adjacent, it will be easy to find all trig ratios. The following are the formulas to find other trigonometric ratios.
For Example
In Figure 1.2, the given sides are
Hypotenuse = 5
Opposite = 3
Adjacent = 4
So the trigonometry ratios will be
sin θ = opposite/hypotenuse = 3/5
cos θ = adjacent/hypotenuse = 4/5
tan θ = opposite/adjacent = 3/4
cscθ = Hypothesis/Opposite = 5/3
secθ = Hypothesis/Adjacent = 5/4
cot θ = Adjacent/Opposite = 4/3
Below is a cleaner look at all trigonometric ratios with their formulas. Students can practice using a trigonometric ratios formula worksheet to strengthen their understanding.
Below is the trigonometric ratios table with respect to angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°.
θ (degrees) | sin θ | cos θ | tan θ | cosec θ | sec θ | cot θ |
0° | 0 | 1 | 0 | Not defined | 1 | Not defined |
30° | 1/2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 | 2 | 2/√3 | √3 |
45° | 1/√2 | 1/√2 | 1 | √2 | √2 | 1 |
60° | √3/2 | 1/2 | √3 | 2/√3 | 2 | 1/√3 |
90° | 1 | 0 | Not defined | 1 | Not defined | 0 |
Trigonometric identities are true for every value of the variable recurring on both sides of the expression or equation. Trigonometric identities involve all trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent. Trigonometric identities include:
Trigonometric Ratios | Trigonometric Identities |
Defined using triangle sides | Equations always true |
Depend on a right-angled triangle | Independent of the triangle |
Used to find values | Used to simplify & prove |
Example: sin θ = opp/hyp | Example: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1 |
Below are common trigonometric identities used to solve complex maths problems.
|
|
|
Sine
Cosine
Tangent
Cotangent
|
Sine
Cosine
Tangent
Cotangent
|
Sine
Cosine
Tangent
Sine × Sine
Cosine × Cosine
Sine × Cosine
|
Sine
Cosine
|
Sine
Cosine
Tangent
|
|
|
|
Get personalised feedback and fix mistakes before your next test.
If sin θ = 3/5, where θ is acute, find cos θ and tan θ.
Solution:
Given:
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse = 3/5
So:
Opposite = 3
Hypotenuse = 5
Using Pythagoras:
Adjacent = √(5² − 3²)
Adjacent = √(25 − 9) = √16 = 4
Now:
Answer:
cos θ = 4/5
tan θ = 3/4
sin 30° + cos 60°
Solution:
We know:
sin 30° = 1/2
cos 60° = 1/2
So:
sin 30° + cos 60° = 1/2 + 1/2 = 1
Answer: 1
(1 − cos 2θ) / sin 2θ = tan θ
Solution:
(1 − cos 2θ) / sin 2θ
= (2 sin²θ) / (2 sin θ cos θ)
= sin θ / cos θ
= tan θ
Hence Proved
sin θ / (1 + cos θ) + (1 + cos θ) / sin θ
Solution:
sin θ / (1 + cos θ) + (1 + cos θ) / sin θ
= sin²θ / (sin θ(1 + cos θ)) + (1 + cos θ)² / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= (sin²θ + (1 + cos θ)²) / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= (sin²θ + (1 + 2 cos θ + cos²θ)) / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= ((sin²θ + cos²θ) + 1 + 2 cos θ) / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= (1 + 1 + 2 cos θ) / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= 2(1 + cos θ) / (sin θ(1 + cos θ))
= 2 / sin θ
= 2 cosec θ
Simplified Identity
Find the value of 9 csc^2θ − 9 cot^2θ.
Solution:
Factor out 9:
9(csc^2θ − cot^2θ)
Using the identity:
1 + cot^2θ = csc^2θ
So,
csc^2θ − cot^2θ = 1
Therefore:
9(1) = 9
1. If sin θ = 3/5, where θ is acute, what is cos θ?
A) 3/4
B) 4/5
C) 5/3
D) 5/4
Correct Answer: B) 4/5
2. Evaluate: sin 30° + cos 60°
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1
D) 2
Correct Answer: C) 1
3. Which of the following is equal to 1 + tan²θ?
A) cosec²θ
B) sec²θ
C) cot²θ
D) sin²θ
Correct Answer: B) sec²θ
4. Find the value of: (sec θ − tan θ)(sec θ + tan θ)
A) 0
B) 1
C) sec²θ
D) tan²θ
Correct Answer: B) 1
5. Evaluate: sin 2θ / (1 + cos 2θ)
A) sin θ
B) cos θ
C) tan θ
D) cot θ
Correct Answer: C) tan θ
Mixt Academy is providing expert tutors for all subjects, including mathematics. We will note the student’s academic requirement first and then match each student with the most suitable online maths tutors who are connected globally on our platform. Flexible timings and easy-to-understand lectures help students achieve higher grades in tests or exams. So, either you need help with your daily homework, or it’s the IGCSE, GCSE or A level, we provide customised support for all curricula and subjects.
Flexible timings, clear teaching, and personalised math support for students.
Trigonometry may seem challenging at the beginning, but with practice and the right steps, it becomes much easier to understand. By learning trigonometric ratios, formulas, and identities, students can solve many math problems quickly and correctly. Remember to practice regularly, use shortcuts like SOH-CAH-TOA, and understand each step instead of memorising blindly. With time and practice, mastering trigonometric ratios will feel simple and rewarding.
The main trigonometric ratios formulas are as follows.
The common trigonometric ratios include sine, cosine and tangent.
Trigonometric ratios deal with the relationship between the angles and side lengths in a right-angle triangle.
The six trigonometric ratios include the core three ratios, sine, cosine, and tangent, and other ratios include cosecant, secant and cotangent.
4 parts of trigonometry refer to the four main categories that trigonometry deals with, which include core right-angle triangle, spherical, plane and analytical trigonometry.

Mixt Academy is a global online tutoring platform that connects students with expert IGCSE, GCSE, and A-Level tutors for one-to-one learning. With flexible scheduling, personalized lesson plans, and experienced teachers from top curricula, Mixt Academy helps students strengthen concepts, improve exam skills, and achieve higher grades with confidence.
IGCSE Chemistry Papers: Common Mistakes & Exam Tips This IGCSE…
IGCSE Extended vs Core Tiers: How to Pick the Right…
Last Month Before IGCSE Exams: A Complete Study Plan Are…
Understanding GCSE Grade Boundaries and How to Prepare? Grade boundaries…
Differences GCSE English Language vs English Literature GCSE English is…
What is GCSE? A Guide for International Students & Parents…
Top Benefits of Completing AS and A Levels Privately Explore…
IB Math: Strategies for Achieving a Level 7 Learn expert…
How to Use OCR Past Papers for Effective Revision? Past…
Complete Guide to the AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification Understanding the…
Everything Students and Parents Must Know About AQA Exams Choosing…
AQA vs Cambridge: Comparing UK and International Exam Boards When…
Hire an Expert Tutor from Just 15$/hr