One of the basic principles of studying chemistry is learning how matter changes. Changes in matter occur every day in the surrounding environments. Melting ice, food cooking and iron rusting are all observable changes in matter. In chemistry, these changes are simplified into two categories: Physical changes vs Chemical changes. This serves as the basis for more complex chemistry principles and is relevant to students learning the difference between physical and chemical changes in class 9.
In this article, you will learn what a physical change is, what a chemical change is, physical vs chemical changes examples, common differences between them, along with key characteristics and identification methods.
A change reflects the alteration in shape, size, colour, state, or chemical makeup of matter. Changes can be classified into two categories based on new substance formation:
It is essential to understand the concepts of physical and chemical changes to successfully answer questions in chemistry and apply these concepts to real life.
A physical change is defined as a change where the only aspects which are modified are the physical characteristics of the substance, and the chemical structure of the substance stays the same.

These common physical change examples highlight that matter may look different, but its chemical nature does not change.
A chemical change is a process in which the formation of one or more new substances takes place because of a change in the chemical composition of the substances involved. Chemical changes occur because of the breaking and new formation of chemical bonds. The new resulting substances will have completely different sets of properties from the original materials.
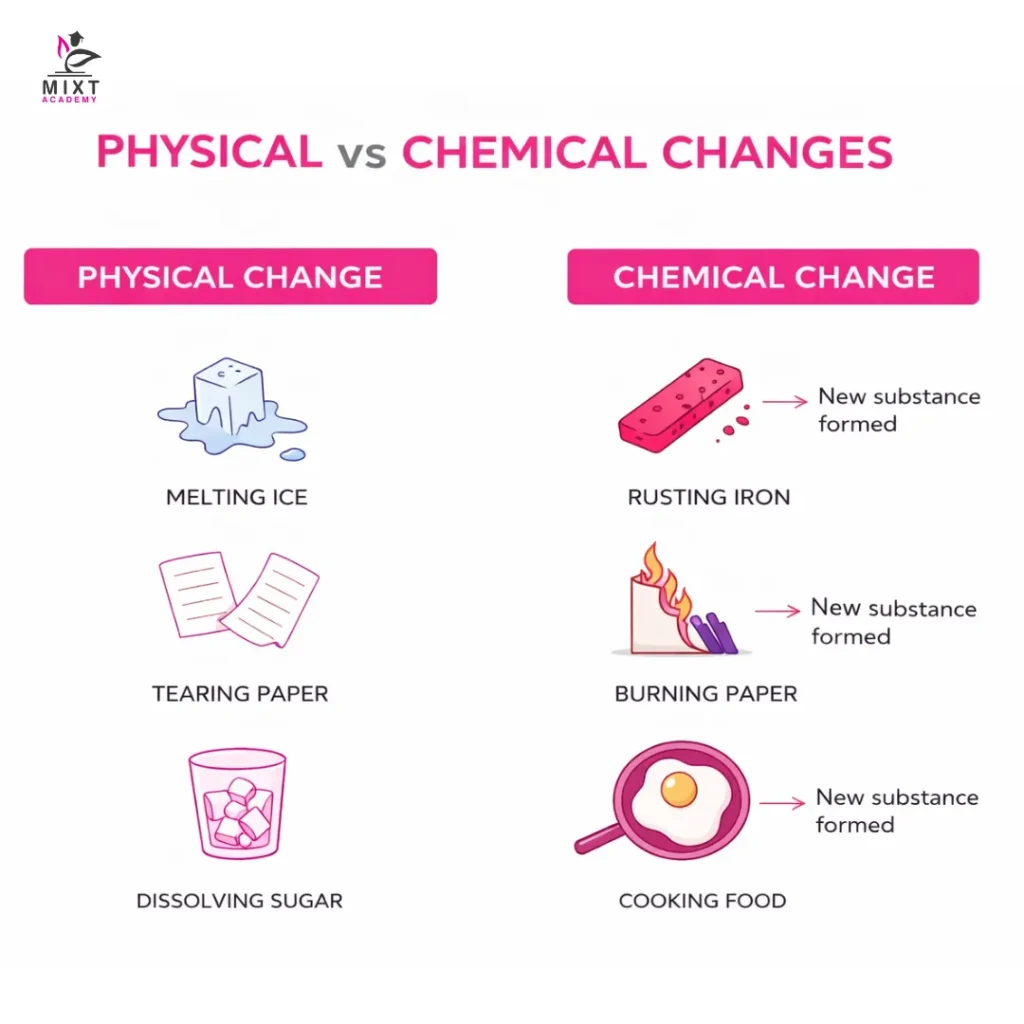
These chemical change examples clearly show the formation of new substances.
| Basis | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| Nature | Change in physical properties | Change in chemical composition |
| New substance | Not formed | Always formed |
| Reversibility | Usually reversible | Mostly irreversible |
| Energy change | Very little or none | Significant energy change |
| Example | Melting ice | Burning wood |
These 5 differences between physical and chemical change are frequently tested in school examinations.
To class 9 students, this topic is a central part of the Chemistry syllabus. Important points to note for the examinations are:
Students are often asked to:
To determine whether a change is physical or chemical, consider the following:
These simple checks help avoid common conceptual errors.
Get step-by-step explanations with real-life examples from expert tutors.
Mixt Academy online Chemistry tutoring is designed to bridge learning gaps through personalised instruction. Students receive:
This approach ensures that students not only learn the difference between physical and chemical change in class 9, but also develop a long-term understanding required for higher classes.
Practice structured notes and comparison charts with guided help.
The most reliable way to identify a chemical change is to understand how new substances are formed.
Access worksheets, doubt-solving sessions, and exam-focused mentoring.
To understand the fundamentals of chemistry, students must analyse the concept of Physical vs Chemical Changes. Chemical changes are when new substances are formed, and physical changes are simply changes in state or appearance. As long as students understand the characteristics of physical vs chemical changes examples, they will confidently answer exam questions and utilise the knowledge in real-life scenarios. With the support of expert Chemistry tutors, conceptual breakdown, and structured guidance from Mixt Academy, the mastery of chemistry is made practical, logical, and simple.
A physical change does not create a new substance. A chemical change creates one or more new substances.
No, it is a physical change because water is still the same chemically.
Yes, the process of rusting makes iron oxide, a new substance with different properties.
Yes, sugar can be recovered by evaporation; this indicates no chemical change.
The concept of Physical vs Chemical Changes is the basis to understand chemical reactions, equations, and laboratory experiments studied in higher classes.
In a physical change, no new substance is formed. In a chemical change, one or more new substances are formed. Physical change is easily reversible i.e original substance can be recovered. Chemical changes are irreversible.

Mixt Academy is a global online tutoring platform that connects students with expert IGCSE, GCSE, and A-Level tutors for one-to-one learning. With flexible scheduling, personalized lesson plans, and experienced teachers from top curricula, Mixt Academy helps students strengthen concepts, improve exam skills, and achieve higher grades with confidence.
IGCSE Chemistry Papers: Common Mistakes & Exam Tips This IGCSE…
IGCSE Extended vs Core Tiers: How to Pick the Right…
Last Month Before IGCSE Exams: A Complete Study Plan Are…
Understanding GCSE Grade Boundaries and How to Prepare? Grade boundaries…
Differences GCSE English Language vs English Literature GCSE English is…
What is GCSE? A Guide for International Students & Parents…
A Level vs AP: Complete Guide to Choosing the Right…
Top Benefits of Completing AS and A Levels Privately Explore…
IB vs A Levels: Which Qualification Is Right for You?…
IB Math: Strategies for Achieving a Level 7 Learn expert…
How to Use OCR Past Papers for Effective Revision? Past…
AQA Physics Equation Sheet: Complete GCSE Guide for Combined Science…
AQA vs Edexcel Complete GCSE Comparison and Guide Choosing between…
Complete Guide to the AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification Understanding the…
Hire an Expert Tutor from Just 15$/hr