Types of education explained with formal, informal,l and non-formal learning examples
Education is the primary driver of both personal development and societal advancement, yet its implementation varies across cultures. Educational systems across the globe develop through the interaction of cultural elements and economic factors, social values and resource distribution, which determine different learning approaches for students and different patterns of social development.
Educational institutions provide structured classroom instruction and skill development through academic programs that extend throughout an individual’s lifetime. Educational programs provide learning opportunities that help students, their families, teachers, and education decision-makers select appropriate learning options for different situations.
The blog, published by Mixt Academy, presents a comprehensive guide to international education systems, explaining different educational pathways and their potential benefits and actual effects on society.
The educational process enables people to acquire knowledge and skills. Moreover, it develops their values and habits, which enable them to grow and participate in society. The education system begins in early childhood and continues until death. At the same time, it develops individuals’ learning, communicative, and problem-solving abilities.
Education exists beyond the boundaries of schools and classrooms. People acquire knowledge through everyday activities, training programs, and self-study outside the formal education system provided by schools and universities. Learning occurs in all environments, including home spaces for private 1-on-1 tutoring, both in-person and online sessions, work locations, and community areas.
In simple terms, education helps people understand the world around them, make better decisions, and improve their quality of life. It plays a vital role in personal development, career opportunities, and building strong, informed societies.
The education system is a lifelong journey through which individuals gain knowledge, develop skills, and build values that help them understand the world and participate meaningfully in society. It is not limited to classrooms or degrees; learning takes place through everyday experiences, reading, observation, and interaction. Education encourages positive behaviour, strengthens critical thinking, and prepares individuals to face real-life challenges with confidence.
Although schools and universities play a central role, education also occurs outside formal institutions. People learn continuously through family, community, work environments, and self-directed study.
The primary goal of education is to nurture an individual’s overall potential. It promotes creativity, ethical values, problem-solving abilities, and informed decision-making, enabling people to adapt to a changing world.
Education is an ongoing process rather than a one-time achievement. It goes beyond examinations and certificates, encouraging awareness, curiosity, and personal development throughout life.
Informal Education: Learning gained through daily activities and life experiences.
Education is recognised globally as a basic human right and a foundation for social progress. It supports economic development, promotes equality, and helps create informed, responsible citizens.
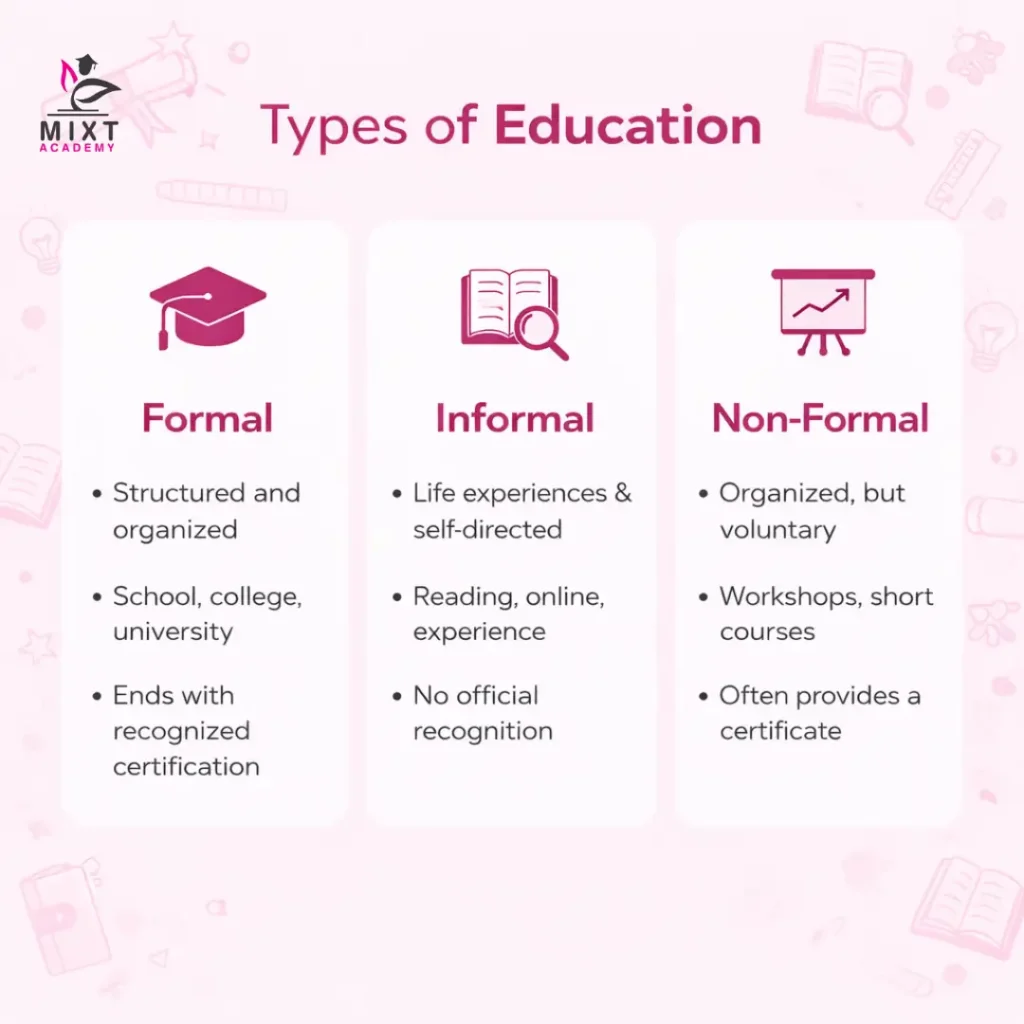
What are the 3 types of education? The three primary types of education are Formal, Informal, and Non-Formal, each playing a unique role in personal and societal development.
Here’s how to apply for a private tuition license in the UAE through MoHRE’s online portal.
Together, these three types of education work in harmony to support the comprehensive development of individuals by combining structured learning, skill acquisition, and experiential growth.
Formal education occurs in schools, colleges, and universities. It follows a set curriculum, is delivered by trained online tutors, and leads to official qualifications. Learning is chronological, organised in grades or levels, and follows a defined timeframe.
Informal education is unplanned and unstructured. It occurs throughout life, often through daily interactions, self-directed learning, family guidance, and practical experiences. It focuses on learning by doing and personal growth rather than formal assessment.
Cost-Free Learning: Informal education typically involves no fees, making it accessible to everyone.
Non-formal education is structured and intentional but takes place outside traditional classrooms. Examples include workshops, vocational training, adult education, and skill-development programs. It is often designed to meet specific learning needs and practical goals.
Join Mixt Academy Online, a trusted global platform connecting students with qualified tutors for personalised learning.
| Particulars | Formal Education | Informal Education | Non-Formal Education |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Structured, institutionalised learning with curriculum and certification | Unstructured, spontaneous learning from daily experiences | Organised learning outside formal schools, skill-based and flexible |
| Aspect | Schools, colleges, universities, and professional degrees | Learning from family, peers, media, and life experiences | Adult literacy programs, vocational courses, community workshops |
| Activities | Classroom teaching, exams, assignments, projects | Conversations, hobbies, observations, self-study | Workshops, practical demonstrations, interactive sessions |
| Feature | Predefined syllabus approved by authorities | No fixed syllabus, learner-driven | Designed for specific skills or knowledge areas |
| Criteria | Degrees, diplomas, academic qualifications | Personal development, life skills, social abilities | Skill acquisition, participation certificates, and practical competencies |
| Sources | Educational institutions, certified teachers | Family, society, environment, media | NGOs, training centres, online platforms, community organisations |
| Methods | Structured instruction, formal assessments | Observation, imitation, trial and error, and discussion | Hands-on practice, interactive learning, flexible assessment |

Professional Development Programs: Targeted training for employees or professionals to upgrade skills, improve workplace performance, and stay current with industry trends and standards.
| Type of Education | Advantages | Dis-advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Formal Education |
Provides recognised qualifications like diplomas, degrees, and certifications. A structured curriculum ensures systematic learning. Taught by trained educators with consistent standards. Prepares students for careers and higher education. Promotes discipline and time management. |
Rigid and less flexible, limiting creativity. Exam-focused, emphasising memorisation over understanding. Often expensive, especially higher education. Learning may lack practical application. Fixed schedules may not suit all learners. |
| Informal Education |
Flexible & self-directed; students follow personal interests. Lifelong learning across all ages. Free or low-cost, widely accessible. Promotes creativity, problem-solving, and practical knowledge. Adaptable to real-life situations. |
Lacks formal recognition or certifications. Outcomes are inconsistent and difficult to measure. Quality depends on initiative and resources. May not provide structured guidance. Harder to use for formal career advancement. |
| Non-Formal Education |
Focused on practical skills and real-life applications. Flexible and accessible for specific groups. Encourages active participation and engagement. May provide skill-based certificates. Bridges gaps between formal and informal learning. |
Limited recognition compared to formal education. Quality may vary by provider. May lack comprehensive theoretical knowledge. Not always systematically progressive. Certificates may not be widely accepted. |
The education system worldwide is continually evolving to meet the needs of modern society. Rapid technological advancements, changing workforce demands, and diverse learning styles are reshaping how education is delivered, making it more flexible, inclusive, and skill-oriented than ever before.
Understanding the types of education, formal, informal, and non-formal, helps students of all ages choose the right path. From structured classroom programs to skill-based, self-directed learning, our trusted online tutoring platform offers flexible, certified online courses and workshops designed to meet diverse educational needs.
Discover 4 types of education, gain practical skills, and achieve personal and professional growth from anywhere in the world. Join Mixt Academy Online Today for Personalised Learning!
In schools, PE is often the only place where every child learns movement skills and stays active. Because curricula vary by state and district, it appears in different models, movement, sport, and fitness education, but all share one goal: preparing students for healthy, active lives through meaningful physical learning.
Understanding the types of education is essential for making informed decisions about learning and careers, from formal education in schools and universities to non-formal education such as workshops. In addition, informal learning through daily experiences uniquely contributes to personal and professional growth.
Exploring the types of education and examples helps students, parents, and online tutors adapt to diverse learning needs. By understanding the 3 types of education and the evolving types of education systems, individuals can choose flexible, skills-oriented learning opportunities.
Platforms like Mixt Academy provide online programs that make quality education accessible worldwide.
The Centre for Allied Health Education primarily offers formal and non-formal education programs focused on healthcare careers. Students receive structured, skill-based training in medical and allied health fields, often combining classroom instruction, practical labs, and hands-on clinical experience. These programs prepare learners for professional certifications, practical healthcare roles, and real-world employment opportunities.
Becoming a veterinarian requires formal education. Students must complete a bachelor’s degree in a relevant science (such as biology or animal science) followed by a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) degree from an accredited veterinary school. This structured program includes classroom learning, laboratory training, and clinical rotations, preparing graduates for licensure and professional practice in animal healthcare.
Mixt Academy is a trusted global platform connecting students with qualified tutors for personalised learning across subjects. Our interactive programs cover formal, non-formal, and informal education, helping students master skills, improve academic performance, and gain confidence in a flexible, supportive online environment.
Educational assessment methods are used to evaluate students’ knowledge, skills, and learning progress. Key types include:
Understanding the types of educational assessment helps educators, students, and parents track progress and enhance learning outcomes.

Mixt Academy is a global online tutoring platform that connects students with expert IGCSE, GCSE, and A-Level tutors for one-to-one learning. With flexible scheduling, personalized lesson plans, and experienced teachers from top curricula, Mixt Academy helps students strengthen concepts, improve exam skills, and achieve higher grades with confidence.
IGCSE Chemistry Papers: Common Mistakes & Exam Tips This IGCSE…
IGCSE Extended vs Core Tiers: How to Pick the Right…
Last Month Before IGCSE Exams: A Complete Study Plan Are…
Understanding GCSE Grade Boundaries and How to Prepare? Grade boundaries…
Differences GCSE English Language vs English Literature GCSE English is…
What is GCSE? A Guide for International Students & Parents…
A Level vs AP: Complete Guide to Choosing the Right…
Top Benefits of Completing AS and A Levels Privately Explore…
IB vs A Levels: Which Qualification Is Right for You?…
IB Math: Strategies for Achieving a Level 7 Learn expert…
How to Use OCR Past Papers for Effective Revision? Past…
AQA Physics Equation Sheet: Complete GCSE Guide for Combined Science…
AQA vs Edexcel Complete GCSE Comparison and Guide Choosing between…
Complete Guide to the AQA GCSE Chemistry Specification Understanding the…
Hire an Expert Tutor from Just 15$/hr